When you’re designing databases – especially physical data models – it’s a good idea to use a testing environment that’s simple to create.
For example, if you’re interested in working with the PostgreSQL database, you don’t need to install it directly on your computer. But you can easily create a test environment using Docker Desktop. I’m happy to say that this is probably the easiest way to create and run a database and also to easily remove the test environment.
Let’s see how easy it is.
You’ll find the simplest method in our step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Install Docker Desktop
First, download and install Docker Desktop on your system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
Once you’ve installed it, go ahead and open it.
Step 2: Find the PostgreSQL Image
Go to the Images tab and click Search images to run.
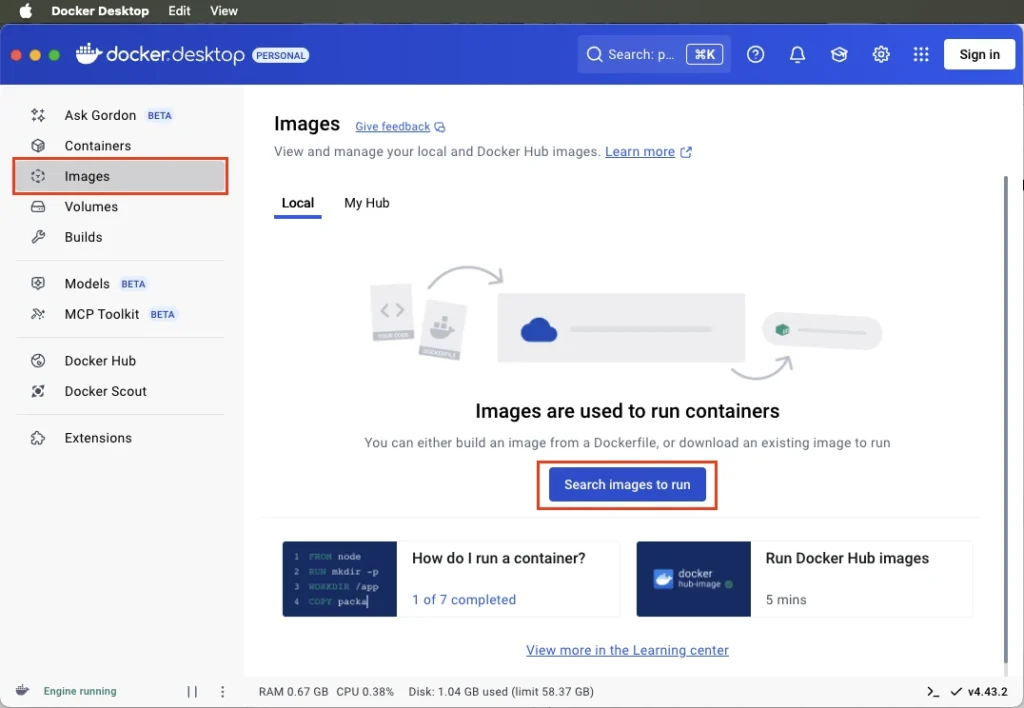
Search for “postgres”. A list of available images will appear. Now you can either pull the image by clicking the Pull button or click the Run button to run the container directly.
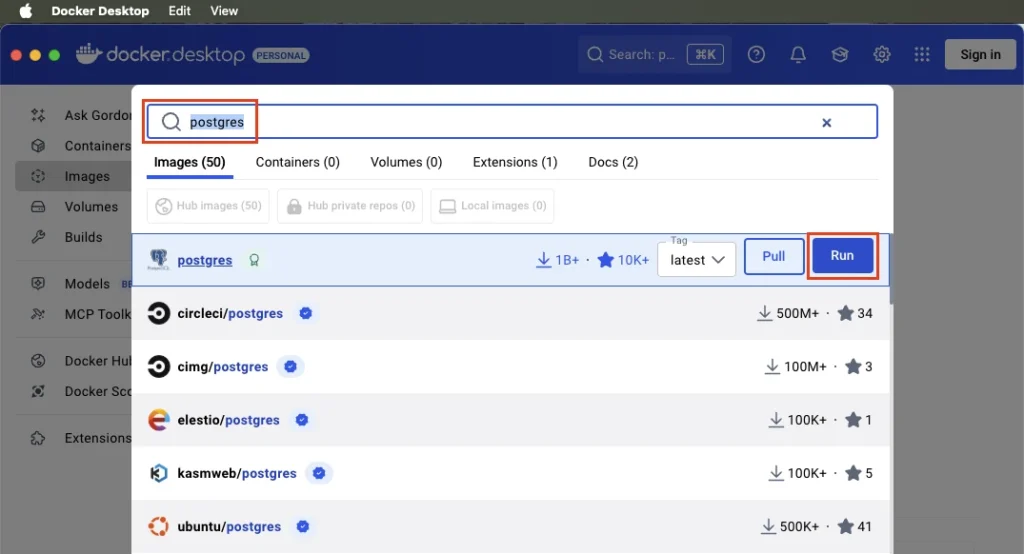
Step 3: Run a container with PostgreSQL settings
After clicking the Run button a new form opens. Define the following optional settings:
- Container name
- Host port – the default for PostgreSQL is 5432, but if the port is not available, set the value to some other value, e.g. 5433.
- Add a new environment variable POSTGRES_PASSWORD and type in the Value. This will be your password for the postgres user.
Then click the Run button on the Run a new container form.
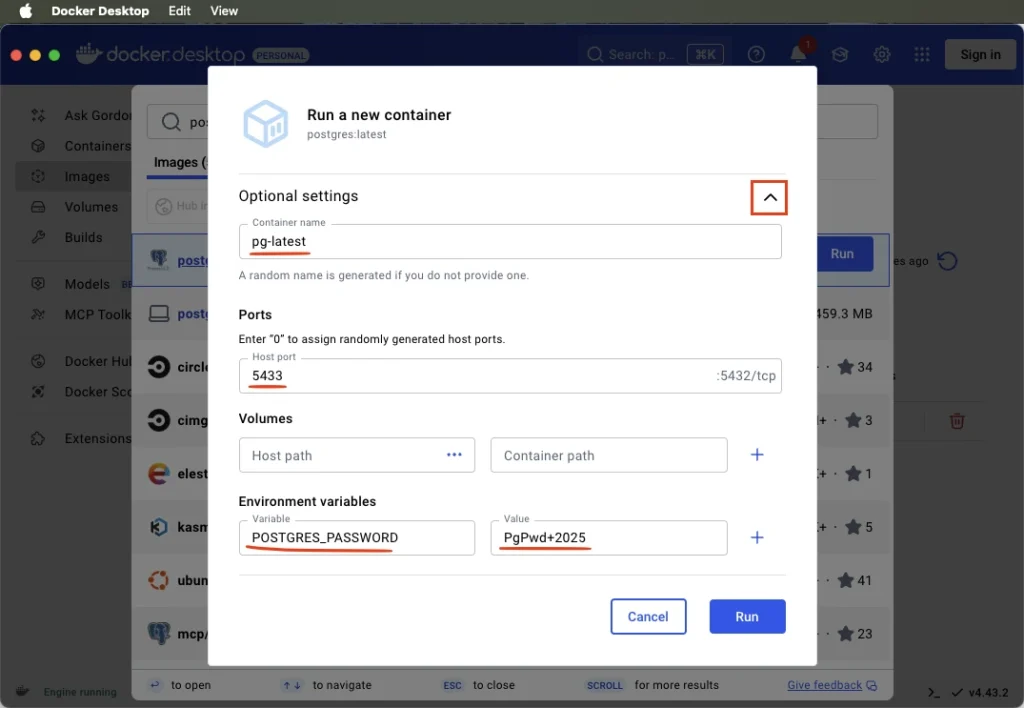
If you check the Containers section, you’ll see the running container there now.
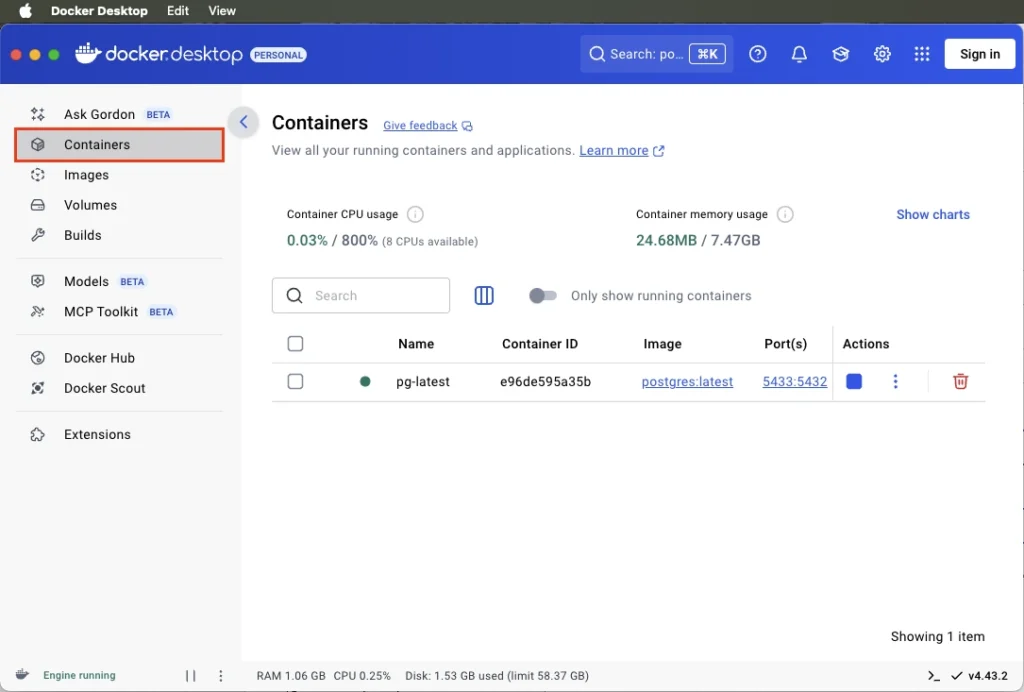
The database is now up and running.
Working with the PostgreSQL database
Now you can create a connection to this database in pgAdmin, VS Code, and run SQL scripts generated from your data model.
If you make a change directly in the database, you can also create a connection in Luna Modeler and update your data model. This will keep your data model in sync.
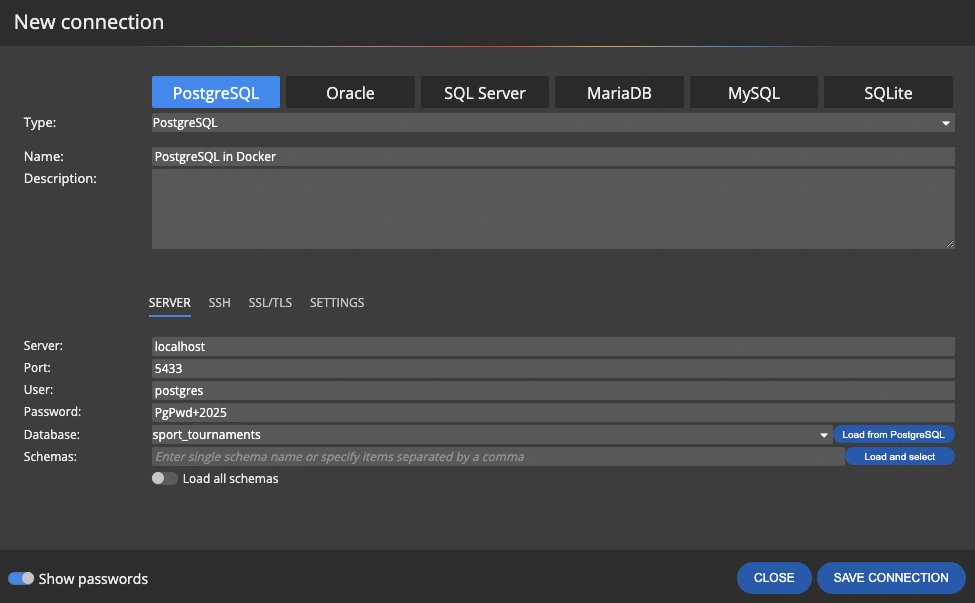
Tip: It is often advisable to update the physical data model, as properties and values that are default for the PostgreSQL database, such as collation and others, are also transferred to the data model.
